Implementing Softmax From Scratch: A Complete Guide for Machine Learning Practitioners
Introduction
In machine learning and deep learning, Softmax is one of the most widely used activation functions, especially in classification problems. If you have ever trained a neural network for multi-class classification—such as digit recognition, sentiment analysis, or image classification—you have almost certainly used Softmax, even if indirectly through a framework like TensorFlow or PyTorch.
Despite its popularity, many practitioners treat Softmax as a “black box.” Understanding how Softmax works from scratch, both mathematically and programmatically, is essential for building strong fundamentals in machine learning. It helps you debug training issues, understand numerical stability problems, and gain deeper intuition about probability-based outputs.
This article provides a step-by-step explanation of Softmax, starting from intuition and math, moving through implementation from scratch, and ending with practical considerations such as numerical stability and gradient computation.
What Is the Softmax Function?
Softmax is a mathematical function that converts a vector of real-valued numbers (called logits) into a probability distribution.
Key Properties of Softmax Output
-
All output values are between 0 and 1
-
The sum of all output values is 1
-
Each value represents the probability of a class
This makes Softmax ideal for multi-class classification, where only one class is correct.
Why Do We Need Softmax?
Consider a neural network’s final layer that outputs raw scores:
These values:
-
Are not probabilities
-
Can be negative or greater than 1
-
Do not sum to 1
Softmax transforms these scores into something like:
Now we can say:
-
Class 0 has a 65% probability
-
Class 1 has a 23% probability
-
Class 2 has a 12% probability
This probabilistic interpretation is crucial for:
-
Loss functions like Categorical Cross-Entropy
-
Model evaluation
-
Decision-making
Mathematical Definition of Softmax
Given an input vector z:
z=[z1,z2,…,zn]z = [z_1, z_2, …, z_n]
The Softmax function for the i-th element is:
Softmax(zi)=ezi∑j=1nezj\text{Softmax}(z_i) = \frac{e^{z_i}}{\sum_{j=1}^{n} e^{z_j}}
Breaking It Down
-
Exponentiation (
e^z)-
Ensures outputs are positive
-
-
Normalization
-
Divides by the sum of all exponentials
-
Ensures outputs sum to 1
-
Understanding Softmax Intuitively
Softmax amplifies differences between values:
-
Larger logits → much higher probabilities
-
Smaller logits → much lower probabilities
For example:
This makes Softmax a confidence amplifier, which is why it is usually used only in the final layer of a classification network.
Implementing Softmax From Scratch (Basic Version)
Let’s start with a simple implementation using Python and NumPy.
Step 1: Import Required Library
Step 2: Define the Softmax Function
Step 3: Test the Function
Output:
This basic version works—but it has a serious flaw.
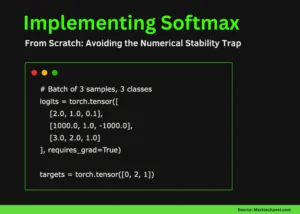
The Numerical Stability Problem
Softmax involves exponentiation, which can easily lead to overflow errors.
Example of the Problem
This will result in:
-
Overflow
-
infvalues -
NaNprobabilities
Why This Happens
The exponential function grows extremely fast:
e1000≈∞ (for computers)e^{1000} \approx \infty \text{ (for computers)}
Numerically Stable Softmax
The standard solution is to subtract the maximum value from the input vector before exponentiation.
Mathematical Insight
Softmax is shift-invariant:
Softmax(z)=Softmax(z−max(z))\text{Softmax}(z) = \text{Softmax}(z – \max(z))
This trick prevents overflow without changing the output probabilities.
Implementing Stable Softmax From Scratch
Test with Large Numbers
Output:
No overflow. No errors. Perfectly stable.
Softmax for Batch Inputs
In real neural networks, we process batches of data, not just single vectors.
Input Shape
Batch Softmax Implementation
Example
Each row now sums to 1 independently.
Softmax and Probability Theory
Softmax is closely related to:
-
Multinomial logistic regression
-
Maximum likelihood estimation
-
Bayesian probability normalization
In essence, Softmax converts unnormalized log probabilities into valid probability distributions.
Softmax vs Sigmoid
| Feature | Softmax | Sigmoid |
|---|---|---|
| Output range | (0, 1) | (0, 1) |
| Sum of outputs | 1 | Not constrained |
| Use case | Multi-class | Binary / multi-label |
| Mutual exclusivity | Yes | No |
Use Softmax when:
-
Only one class is correct
Use Sigmoid when:
-
Multiple classes can be correct simultaneously
Computing the Gradient of Softmax (Conceptual)
Softmax is almost always used with Cross-Entropy Loss.
The gradient of Softmax alone is complex:
∂Si∂zj={Si(1−Si),i=j−SiSj,i≠j\frac{\partial S_i}{\partial z_j} = \begin{cases} S_i (1 – S_i), & i = j \\ – S_i S_j, & i \neq j \end{cases}
This results in a Jacobian matrix, making manual backprop expensive.
Practical Insight
Frameworks combine Softmax + Cross-Entropy into a single, optimized operation, simplifying gradients and improving stability.
Implementing Softmax Gradient (Educational)
This is mainly for learning purposes, not production use.
Common Mistakes When Implementing Softmax
-
Ignoring numerical stability
-
Forgetting batch dimensions
-
Applying Softmax in hidden layers
-
Using Softmax for multi-label problems
-
Computing Softmax twice (once manually, once in loss)
Where Softmax Is Used in Practice
-
Image classification (CNNs)
-
NLP tasks (token prediction)
-
Speech recognition
-
Recommendation systems
-
Reinforcement learning policies
Almost every modern AI system relies on Softmax at some level.
Softmax in Popular Frameworks
-
PyTorch:
torch.nn.Softmax -
TensorFlow:
tf.nn.softmax -
JAX:
jax.nn.softmax
All of them:
-
Use numerical stability tricks
-
Are highly optimized in C++/CUDA
-
Fuse Softmax with Cross-Entropy when possible
Why You Should Still Learn Softmax From Scratch
Even though libraries exist, implementing Softmax yourself helps you:
-
Build strong ML fundamentals
-
Debug exploding/vanishing gradients
-
Understand confidence calibration
-
Read research papers more effectively
-
Perform well in ML interviews
Conclusion
Softmax may look simple, but it is one of the most important building blocks in machine learning. By implementing Softmax from scratch, you gain insight into probability normalization, numerical stability, and the foundations of classification models.
Understanding Softmax deeply transforms you from someone who uses machine learning libraries into someone who truly understands them.
If you master Softmax, concepts like Cross-Entropy, attention mechanisms, and transformer outputs become far easier to grasp.
For quick updates, follow our whatsapp –https://whatsapp.com/channel/0029VbAabEC11ulGy0ZwRi3j
https://bitsofall.com/recursive-language-models-rlms/
https://bitsofall.com/ai-interview-series/
TII Abu Dhabi Released Falcon H1R-7B — a compact reasoning model that punches above its weight