Deepfake Detection: Technologies, Challenges, and the Future of Trust in the Digital Age
Introduction
In the last decade, artificial intelligence has transformed how digital media is created and consumed. Among the most disruptive outcomes of this transformation is deepfake technology—AI-generated or AI-manipulated images, videos, and audio that convincingly imitate real people. While deepfakes have legitimate uses in entertainment, accessibility, and education, their misuse poses serious threats to privacy, democracy, cybersecurity, and public trust.
This has made deepfake detection one of the most critical challenges in modern AI research and digital forensics. Governments, technology companies, researchers, and media organizations are racing to develop systems capable of identifying manipulated content before it causes harm.
This article provides a comprehensive, in-depth exploration of deepfake detection: what deepfakes are, how they are created, why detection is difficult, the technologies used to identify them, real-world applications, current limitations, and what the future holds.
What Are Deepfakes?
Deepfakes are synthetic media generated using deep learning techniques—primarily generative adversarial networks (GANs) and diffusion models—to replace or manipulate a person’s likeness in images, videos, or audio.
Common types of deepfakes include:
-
Face swap videos – One person’s face is replaced with another’s.
-
Lip-sync deepfakes – Mouth movements are altered to match fabricated speech.
-
Voice cloning – AI replicates a person’s voice using minimal audio samples.
-
Synthetic avatars – Fully AI-generated humans that appear realistic.
-
Text-to-video deepfakes – AI generates videos directly from textual prompts.
The realism of modern deepfakes has reached a point where even trained professionals can struggle to identify them without technical tools.
Why Deepfake Detection Matters
Deepfake detection is no longer a niche technical problem—it is a societal necessity.
1. Threats to Democracy
Fake videos of political leaders making false statements can influence elections, incite violence, or manipulate public opinion.
2. Financial Fraud and Cybercrime
Voice deepfakes are increasingly used in CEO fraud, social engineering attacks, and identity theft.
3. Reputation and Privacy Violations
Non-consensual deepfake videos can destroy personal and professional reputations, especially in cases involving explicit content.
4. Media Trust Erosion
As fake content becomes harder to detect, public trust in legitimate journalism and visual evidence erodes.
Deepfake detection acts as a digital immune system, protecting society from large-scale misinformation and deception.
How Deepfakes Are Created (Detection Context)
Understanding detection requires understanding generation.
Deepfakes are commonly created using:
-
GANs – Two neural networks compete: one generates fake media, the other tries to detect it.
-
Autoencoders – Learn compressed facial representations and reconstruct them onto another face.
-
Diffusion models – Generate media by iteratively refining noise into realistic outputs.
-
Neural voice synthesis models – Mimic vocal tone, cadence, and emotion.
Each generation technique leaves behind subtle artifacts—imperfections that detection systems aim to uncover.
Core Principles of Deepfake Detection
Deepfake detection systems analyze inconsistencies that humans may overlook, such as:
-
Pixel-level anomalies
-
Temporal inconsistencies across video frames
-
Physiological impossibilities
-
Audio-visual mismatches
-
Metadata irregularities
Detection is typically framed as a binary classification problem: real vs. fake.
Major Techniques Used in Deepfake Detection
Early deepfakes often contained visible flaws:
-
Blurry edges around faces
-
Inconsistent lighting or shadows
-
Unnatural skin textures
Modern deepfakes are more refined, but microscopic pixel inconsistencies still exist and can be detected using AI models.
2. Facial Landmark and Geometry Detection
AI models analyze facial landmarks such as:
-
Eye spacing
-
Jaw alignment
-
Lip symmetry
-
Head pose consistency
Deepfakes may distort these relationships subtly, especially during head movement or facial expressions.
3. Temporal Consistency Analysis
Videos are not just images—they are sequences.
Detection models examine:
-
Frame-to-frame motion
-
Expression continuity
-
Head and body synchronization
Deepfakes may look perfect in a single frame but reveal flaws over time.
4. Physiological Signal Detection
Human bodies exhibit involuntary signals, such as:
-
Eye blinking patterns
-
Heartbeat-induced skin color changes (photoplethysmography)
-
Micro facial muscle movements
Deepfakes often fail to replicate these accurately, making them valuable detection cues.
5. Audio Deepfake Detection
Voice deepfakes are analyzed using:
-
Spectral features
-
Pitch consistency
-
Breathing patterns
-
Emotional timing mismatches
Synthetic voices often lack natural imperfections present in real human speech.
6. Multimodal Detection (Audio + Video)
Advanced systems combine:
-
Lip movement vs. speech alignment
-
Facial expression vs. vocal emotion
-
Timing synchronization across modalities
Multimodal detection is significantly more robust than single-channel approaches.
Machine Learning Models Used for Detection
Deepfake detection relies heavily on advanced ML architectures:
-
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) – Image and video frame analysis
-
Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) – Temporal pattern detection
-
Transformers – Long-range dependency modeling
-
Vision Transformers (ViTs) – Global visual context understanding
-
Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) – Facial landmark relationships
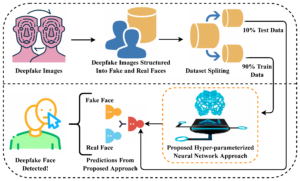
These models are trained on massive datasets containing both real and fake media.
Datasets for Deepfake Detection Research
High-quality datasets are essential for training reliable detectors:
-
Face manipulation datasets
-
Synthetic speech datasets
-
Cross-dataset benchmark collections
-
Real-world social media video datasets
Challenges include dataset bias, outdated generation methods, and lack of diversity in faces, languages, and lighting conditions.
Real-World Applications of Deepfake Detection
Automated detection systems flag or remove manipulated content before it goes viral.
2. Financial Institutions
Banks deploy voice authentication systems to detect synthetic audio fraud.
3. Journalism and Fact-Checking
Newsrooms use forensic AI tools to verify the authenticity of images and videos.
4. Law Enforcement and Legal Systems
Deepfake detection assists in digital evidence validation and cybercrime investigations.
5. Corporate Security
Executives are protected from impersonation-based social engineering attacks.
Challenges in Deepfake Detection
Despite rapid progress, detection remains an arms race.
1. Rapid Improvement of Generative Models
As generators improve, artifacts become harder to detect.
2. Generalization Problems
A model trained on one type of deepfake may fail on new techniques.
3. Adversarial Attacks
Attackers intentionally design deepfakes to bypass detection systems.
4. Computational Cost
Real-time detection at scale requires significant infrastructure.
5. False Positives
Incorrectly labeling real content as fake can damage credibility and trust.
Detection vs. Prevention: A Broader Strategy
Detection alone is not enough. A holistic approach includes:
-
Content provenance systems (cryptographic signatures)
-
Watermarking of AI-generated media
-
Media literacy education
-
Legal and regulatory frameworks
-
Responsible AI development practices
Together, these measures create multiple layers of defense.
The Role of Regulations and Ethics
Governments worldwide are beginning to regulate synthetic media:
-
Mandatory disclosure of AI-generated content
-
Legal consequences for malicious deepfake creation
-
Protection laws for victims of non-consensual deepfakes
Ethical AI development emphasizes transparency, consent, and accountability.
The Future of Deepfake Detection
-
Real-time detection at the edge (devices and browsers)
-
Universal content authenticity standards
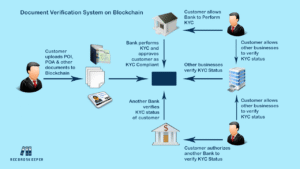
-
Blockchain-based media verification
-
AI watermarking embedded at generation time
-
Collaborative global detection networks
Ultimately, the goal is not just detecting fakes, but restoring trust in digital reality.
Conclusion
Deepfake detection stands at the intersection of artificial intelligence, cybersecurity, ethics, and society. As synthetic media becomes increasingly indistinguishable from reality, detection technologies play a crucial role in protecting truth, identity, and trust.
While no detection system is perfect, ongoing research, combined with regulation, education, and responsible AI practices, offers a path forward. In the digital age, the ability to verify what is real may become just as important as the ability to create.
Deepfake detection is not merely a technical challenge—it is a foundational pillar for the future of information integrity.
For quick updates, follow our whatsapp –https://whatsapp.com/channel/0029VbAabEC11ulGy0ZwRi3j
https://bitsofall.com/gemini-3-flash-rapid-ai-apps/
https://bitsofall.com/next-generation-research/