What Are Context Graphs?
The Missing Layer Between Data, Memory, and Intelligence
Artificial intelligence has become remarkably good at processing information—but it still struggles with something humans do effortlessly: understanding context.
A sentence, a conversation, a task, or even a decision rarely exists in isolation. Meaning is shaped by relationships, history, intent, environment, and prior knowledge. This is where Context Graphs come into play.
Context graphs are emerging as one of the most powerful conceptual tools in modern AI systems, especially in LLMs, autonomous agents, retrieval systems, personalization engines, and long-term memory architectures.
In this article, we’ll deeply explore:
-
What context graphs are
-
How they differ from knowledge graphs
-
Why they matter for modern AI
-
How they’re built
-
Real-world use cases
-
And how they may define the future of intelligent systems
Understanding the Core Idea of Context
Before diving into graphs, let’s define context.
Context is not just “extra information.” It includes:
-
Who is involved
-
What has happened before
-
What is happening now
-
Why something matters
-
How elements relate to each other
-
What constraints or goals exist
Humans constantly build mental context graphs:
-
You remember a conversation because of who said it
-
You interpret words differently based on tone and history
-
You connect new ideas to existing knowledge
AI, traditionally, does not do this well—unless we explicitly model context.
What Are Context Graphs?
A Context Graph is a structured, dynamic representation of contextual information where:
-
Nodes represent entities, events, concepts, states, or memories
-
Edges represent relationships, dependencies, relevance, or temporal links
-
The graph evolves over time as new context is added
In simple terms:
A context graph captures “what matters right now” and how it connects to everything else.
Unlike static data structures, context graphs are:
-
Time-aware
-
Goal-oriented
-
Situation-dependent
-
Continuously updated
Context Graphs
-
Store situational relevance
-
Highly dynamic
-
Answer “What matters right now and why?”
-
Example: Paris → relevant because → user is planning a trip next week
Key Differences at a Glance
| Aspect | Knowledge Graph | Context Graph |
|---|---|---|
| Nature | Static | Dynamic |
| Focus | Truth | Relevance |
| Time-aware | Limited | Strongly |
| Personalization | Low | High |
| Goal-driven | No | Yes |
Think of it this way:
-
Knowledge graphs know the world
-
Context graphs understand the moment
Why Context Graphs Matter in Modern AI
Large Language Models are powerful—but they are context-limited by default.
Even with long context windows, models:
-
Forget earlier interactions
-
Lose task objectives
-
Mix unrelated information
-
Fail to maintain long-term coherence
Context graphs solve this by acting as a persistent, structured memory layer.
Key Benefits
1. Long-Term Memory Without Prompt Bloat
Instead of stuffing everything into a prompt, relevant nodes are activated dynamically.
2. Better Reasoning
Graphs preserve relationships, enabling multi-hop reasoning:
“If A depends on B, and B changed, what happens to A?”
3. Personalization
User preferences, habits, tone, and history become connected context—not isolated logs.
4. Reduced Hallucinations
When the model reasons over grounded context, errors drop significantly.
Anatomy of a Context Graph
Let’s break it down.
Nodes Can Represent:
-
Users
-
Tasks
-
Goals
-
Documents
-
Conversations
-
Events
-
States
-
Decisions
-
Emotions (in some systems)
Edges Can Represent:
-
Temporal order (before, after)
-
Causality (leads to, depends on)
-
Relevance (important to, related to)
-
Ownership (belongs to)
-
Priority (blocks, enables)
Metadata Often Includes:
-
Timestamp
-
Confidence score
-
Source
-
Expiry or decay factor
-
Importance weight
This allows the graph to grow, shrink, and re-weight itself over time.
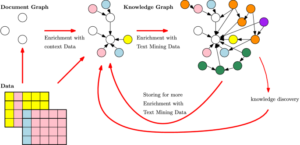
How Context Graphs Are Built
There is no single implementation—but most follow a similar pipeline.
1. Context Extraction
Information is extracted from:
-
User input
-
System events
-
External tools
-
Retrieved documents
-
Agent actions
NLP models identify entities, intents, and signals.
2. Context Normalization
Raw input is transformed into standardized representations:
-
“Book flight” → travel intent
-
“Next Friday” → timestamp
3. Graph Construction
New nodes are:
-
Added
-
Linked
-
Updated
-
Or merged with existing ones
Irrelevant or outdated nodes may decay or be pruned.
4. Context Retrieval
When reasoning or responding:
-
Only relevant subgraphs are activated
-
The AI never sees the entire graph—only what matters
Context Graphs in AI Agents
Autonomous AI agents rely heavily on context graphs.
An agent must track:
-
Current goal
-
Subtasks
-
Tool usage
-
Errors
-
Environment state
-
Past decisions
Without a context graph:
-
Agents loop endlessly
-
Forget objectives
-
Re-do completed tasks
With a context graph:
-
The agent knows where it is, why, and what’s next
This is why many modern agent frameworks quietly revolve around context graph architectures—even if they don’t use the term explicitly.
Context Graphs in Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)
Traditional RAG retrieves documents based on similarity.
Context-aware RAG:
-
Uses the context graph to decide what to retrieve
-
Connects retrieved data to existing goals and history
-
Avoids irrelevant information overload
For example:
The same query can retrieve different documents depending on user role, prior conversation, and task stage.
Context Graphs for Personalization
Context graphs enable deep personalization without surveillance.
Instead of raw data tracking:
-
Preferences become weighted nodes
-
Interests decay naturally
-
Temporary context expires
This allows systems to be:
-
Adaptive
-
Respectful of user intent
-
Less creepy
-
More human-like
Real-World Use Cases
1. Conversational AI
Maintains topic continuity across long conversations.
2. Developer Assistants
Tracks project state, files, errors, and decisions.
3. Healthcare AI
Models patient history, symptoms, treatments, and temporal changes.
4. Enterprise Workflow Automation
Understands dependencies across teams, tools, and timelines.
5. Education Platforms
Learns how a student understands concepts—not just what they answered.
Context Decay and Forgetting (A Feature, Not a Bug)
One of the most important ideas in context graphs is controlled forgetting.
Not all context should live forever.
Modern systems implement:
-
Time-based decay
-
Relevance-based pruning
-
Goal-completion cleanup
This mirrors human cognition:
-
You remember what matters
-
You forget what doesn’t
Context Graphs and Explainability
Because context graphs are structured, they enable:
-
Traceable reasoning paths
-
Decision explanations
-
Debuggable AI behavior
Instead of:
“The model decided X”
You get:
“X was decided because A → B → C under constraint D”
This is crucial for:
-
Regulated industries
-
Trustworthy AI
-
Auditing and compliance
Challenges and Limitations
Context graphs are powerful—but not trivial.
Major Challenges:
-
Scalability
-
Graph maintenance cost
-
Context pollution
-
Incorrect relevance weighting
-
Privacy concerns
The hardest problem is deciding what matters—a deeply subjective question.
The Future of Context Graphs
Context graphs are becoming the invisible backbone of advanced AI.
We are moving toward systems where:
-
LLMs generate language
-
Context graphs provide grounding
-
Agents reason over structured memory
-
Intelligence becomes situational, not just statistical
In the long run, context graphs may matter more than model size.
Final Thoughts
Context graphs represent a fundamental shift in AI design:
From pattern recognition → to situational understanding
They bring AI closer to how humans think—not by copying the brain, but by modeling relevance, memory, and relationships.
As AI systems grow more autonomous, persistent, and personalized, context graphs will be the difference between smart tools and truly intelligent systems.
For quick updates, follow our whatsapp –https://whatsapp.com/channel/0029VbAabEC11ulGy0ZwRi3j
https://bitsofall.com/nouscoder-14b-competitive-programming/
https://bitsofall.com/vercel-releases-agent-skills-ai-coding/