TII Abu Dhabi Released Falcon H1R-7B — a compact reasoning model that punches above its weight
On January 5, 2026, Abu Dhabi’s Technology Innovation Institute (TII) unveiled Falcon H1R-7B, a deliberately compact — but high-performance — large language model that reframes the “bigger is better” narrative in reasoning AI. Built as a 7-billion-parameter decoder model, Falcon H1R-7B is being presented by its creators as a new Pareto-efficient point: strong reasoning and instruction following while requiring far less compute and memory than many 30B+ giants. The model was published with open weights and technical documentation, making it immediately available to researchers and developers. tii.ae+1
What Falcon H1R-7B is (and what it’s not)
Falcon H1R-7B is not merely a shrunken copy of a larger Falcon model. TII framed it as a reasoning-specialized variant developed on top of the Falcon-H1 family, trained and fine-tuned with methods geared toward long, multi-step reasoning traces. Practically this means the team focused on architectures, training curricula, and fine-tuning recipes that help the model think through complex chains of logic — math problems, programming puzzles, and multi-step instruction tasks — rather than optimizing for raw scale or parameter count alone. The release includes both a technical blog and an open model card that explain training choices and evaluation results. Hugging Face+1
Key technical highlights — why the model matters
Several concrete features set Falcon H1R-7B apart:
-
7 billion parameters: small enough to run on modest GPU hardware and enable wider, low-latency deployment compared with much larger models. Hugging Face
-
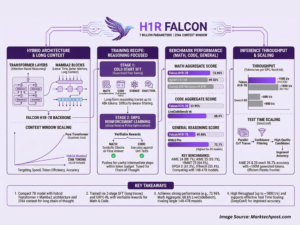
Large context window (reported up to 256k tokens): this allows the model to process extremely long documents or long chains of reasoning without truncating vital context — an important advantage for tasks like code reasoning, long-form analysis, or agent memory. MarkTechPost+1
-
Hybrid architecture and targeted training: TII describes a hybrid approach (a family of architectural and algorithmic choices often referenced as Transformer–Mamba or similar hybrids in their technical narrative) combined with cold-start supervised fine-tuning, long-trace instruction data, and reinforcement learning scaling (GRPO) to sharpen reasoning abilities. These choices are explicitly aimed at improving multi-step logical performance without ballooning parameter counts. Hugging Face+1
-
Open weights and accessible license: the model and weights are available via public model hubs, encouraging reproducibility, community audits, and downstream innovation. This openness was emphasized in TII’s release and on Hugging Face. Business Wire+1
Together, these properties make Falcon H1R-7B a compelling option for teams that need strong reasoning but also care about deployment cost, latency, and the ability to run locally or at the edge.
How it performs: benchmarks and surprising wins
TII’s announcement and independent reporting emphasize that Falcon H1R-7B outperforms many larger models on targeted reasoning benchmarks. Examples highlighted in coverage include strong results in – (AIME-style challenges), coding and program synthesis tests, and logic/instruction following evaluations. Reporters and the institute itself compared the model’s scores favorably against models with many times the parameter count — often calling out cases where the 7B Falcon matched or exceeded 15B–33B rivals on specific tasks. ChannelLife Australia+1
A few important caveats about benchmark reporting:
-
Benchmarks are task-specific. A model that excels on reasoning and math benchmarks may not be the absolute best on general conversational metrics, safety filters, or domain-specific knowledge tests.
-
Comparison methodology matters: datasets used, prompt engineering, temperature and decoding settings, and whether chains-of-thought traces were allowed or elicited can all shift results. TII published technical notes to explain their methodology, but independent replication by the community will be essential to confirm the breadth of these claims. Business Wire+1
Why design for “reasoning first” matters
The Falcon H1R-7B release is part of a broader trend: teams are increasingly optimizing model capabilities per compute rather than pursuing raw parameter count. There are several practical reasons this matters:
-
Deployability — Smaller, efficient models lower the barrier for running locally or on smaller cloud instances, improving privacy (on-prem execution), latency (realtime apps), and cost. Falcon H1R-7B’s 7B size makes on-prem and edge use realistic for many enterprises. ChannelLife Australia
-
Energy and sustainability — Less compute per inference translates to lower energy consumption and carbon cost, an increasingly important consideration for responsible AI. TII explicitly highlights memory and energy efficiency as design goals. ChannelLife Australia
-
Specialized excellence — Concentrating model capacity and training objective on reasoning problems can produce outsized gains in domains where chain-of-thought and multi-step logic are needed (math tutoring, debugging, theorem-style reasoning, etc.). Falcon
For organizations building assistants, coding copilots, research tools, or embedded inference systems, these tradeoffs are attractive: a model that reasons well while fitting realistic resource envelopes unlocks new product designs.
Use cases where Falcon H1R-7B shines
Based on its design and reported benchmarks, here are practical applications that stand to benefit:
-
Math tutoring and assessment: multi-step problem solving with explicit chain-of-thought support. ChannelLife Australia
-
Code reasoning and generation: extended context windows help the model reason about large codebases or long debugging sessions. Benchmark wins on programming tests make this a promising area. MarkTechPost
-
Document understanding and summarization: a 256k context window opens the door to summarizing books, long legal contracts, or multi-document corpora in a single pass. MarkTechPost
-
Agentic systems and multi-step workflows: planning over long horizons (e.g., task planning with memory) benefits from both efficient reasoning and long contexts. Falcon
-
On-device assistants and privacy-sensitive deployments: organizations that cannot send sensitive data to third parties can host a compact reasoning engine on-prem. ChannelLife Australia
Openness, reproducibility, and the research community
One of the most consequential aspects of the release is TII’s decision to make Falcon H1R-7B available with open weights and to publish technical explanations of the training pipeline. This fosters several healthy outcomes:
-
Independent verification — researchers can reproduce benchmark runs, test failure modes, and verify claimed performance. Hugging Face hosts the model card and distribution which accelerates uptake and auditing. Hugging Face+1
-
Broader innovation — smaller, well-documented models reduce friction for academics, startups, and hobbyists to experiment, fine-tune, and build new applications without huge infrastructure costs. Business Wire
-
Community safety review — open weights allow red-teams and safety researchers to probe for vulnerabilities, biases, and unexpected behavior more effectively than closed offerings. TII’s public blog and the model hub provide starting points for such work. tii.ae
That said, openness also raises responsibility questions: as powerful reasoning models become more accessible, stakeholders must invest in guardrails (content filters, usage policies, watermarking, and monitoring) to mitigate misuse.
Limitations and responsible deployment considerations
No model is perfect, and TII’s own materials and press coverage point to limitations and the need for caution:
-
General knowledge and hallucinations: reasoning prowess doesn’t eliminate hallucinations or incorrect factual claims. Applications should use retrieval, grounding, and verification layers when honesty is important. Business Wire
-
Benchmark scope: excelling on math and code benchmarks is significant but does not guarantee similar performance on open-ended conversational tasks, creative writing, or culturally sensitive reasoning. Venturebeat
-
Safety and bias: small models can still encode harmful biases or be prompted into unsafe behaviors. Deployers must apply the usual mitigations (filtering, human-in-the-loop verification for critical outputs, and usage constraints). Business Wire
How the release fits into the global landscape
Falcon H1R-7B is part of a broader diversification in the LLM ecosystem. In 2024–2026 we’ve seen both massive, multi-hundred-billion parameter models and a countervailing wave of compact, capability-dense models optimized for efficiency. TII’s announcement demonstrates the UAE’s growing role as a research and open-source contributor in the AI field, publishing competitive models and making them available broadly. Industry coverage framed the model as a demonstration that architectural and training ingenuity can yield step-function improvements in reasoning without scaling parameters dramatically. Venturebeat+1
Practical advice for developers and organizations
If you’re considering experimenting with Falcon H1R-7B, here’s a pragmatic checklist:
-
Start with the model card and technical blog — TII’s official release and the Hugging Face blog are the best first reads for details on training, license, and suggested usage. tii.ae+1
-
Evaluate on your tasks — run the model on representative inputs (math, code, long-doc tasks) using the same prompt engineering and decoding settings you’ll use in production. Benchmarks are useful, but your task matters most. Hugging Face
-
Add grounding — combine the model with retrieval or tool-use to reduce hallucinations for fact-heavy tasks.
-
Monitor behavior — build logging, human review, and rollback paths; small models still fail in surprising ways.
-
Consider fine-tuning — H1R was built with fine-tuning in mind; if your use case requires domain knowledge or special behavior, supervised fine-tuning or RL-based calibration can help. Hugging Face
The bigger picture: efficiency as a strategic advantage
Falcon H1R-7B’s emergence reinforces a strategic lesson: efficiency is a product feature. For many real-world applications, latency, cost, and the ability to run privately matter more than incremental gains on generic benchmarks. Models that deliver strong reasoning per compute unit will likely find immediate traction across education, enterprise search, developer tooling, and embedded AI.
Conclusion — a meaningful step, not the last word
TII’s Falcon H1R-7B is an important addition to the model landscape: an open, compact reasoning specialist that challenges the instinct to equate size with intelligence. While the community will need to reproduce and stress-test TII’s claims, the model’s design goals (reasoning, long context, efficiency) align with clear real-world needs. For builders and researchers who want to push multi-step reasoning into deployable products, Falcon H1R-7B is a model worth testing now — and watching closely as the community explores its strengths and exposes its limits. tii.ae+1
Sources & further reading
-
TII announcement and press release. tii.ae
-
Hugging Face blog and model page for Falcon H1R-7B (technical notes, weights). Hugging Face+1
-
Industry coverage and analysis (VentureBeat, ChannelLife, ITBrief). Venturebeat+1
For quick updates, follow our whatsapp –
https://whatsapp.com/channel/0029VbAabEC11ulGy0ZwRi3j
https://bitsofall.com/ai-interview-series/
https://bitsofall.com/recursive-language-models-rlms/
Tiny AI Models: How Small Is the New Big Thing in Artificial Intelligence?
Tesla Loses Market Lead: How the EV Pioneer Is Facing Its Toughest Competition Yet